Online prediction using GCP’s Vertex AI
Serve and process real-time data with a Tensorflow model using Pub-Sub, Cloud Dataflow, BigQuery and Vertex AI.
In this project, we are predicting the travel fare when a user books a cab. Unlike traditional pricing calculation, here the price is calculated dynamically based on multiple parameters, including the feature number of trips in the last 5 minutes, which acts as a proxy for real-time traffic.
Table of Content
- Architecture
- Data Ingestion
- Model Deployment
- Prediction
1. Architecture
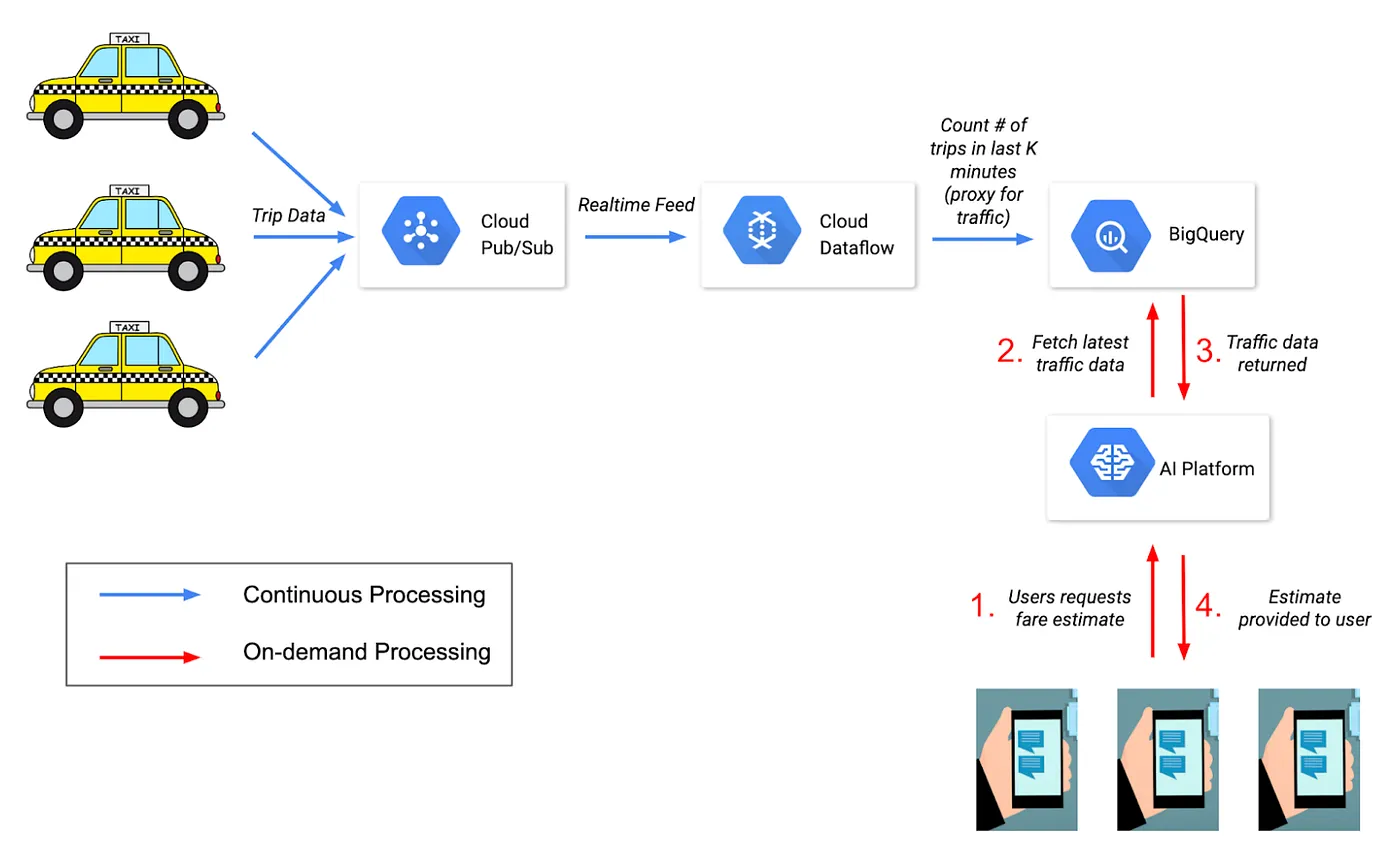
The whole system can be divided into two parts
- Ingesting continuous feed of taxi trip data
- Predicting on-demand fare requests
2. Data Ingestion
For the data ingestion part, we will need Pub/Sub, Dataflow and Big query. Let's configure the required services one by one.
Pub-Sub
Pub/Sub is used for streaming analytics and data integration pipelines to ingest and distribute data. It is equally effective as a messaging-oriented middleware for service integration or as a queue to parallelize tasks. Read more about the core concepts like - topics, subscription, publisher, etc.
Here Pub/Sub will be used as a messaging bus that receives and stores recently completed taxi trips.
import logging
from google import api_core
from google.cloud import pubsub_v1 as pubsub
def get_pubsub_client(gcp_project_id, topic="taxi_rides"):
""" Get topic if already exists or else create a new one
"""
publisher = pubsub.PublisherClient()
topic_name = publisher.topic_path(gcp_project_id, topic)
try:
publisher.get_topic(topic_name)
logging.info("Reusing pub/sub topic %s", topic)
except api_core.exceptions.NotFound:
publisher.create_topic(topic_name)
logging.info("Creating pub/sub topic %s", topic)
return publisher
Since we cannot get live taxi trip data we will create a python script that randomly generates trip data and pushes it to the Pub/Sub.
PROJECT_ID=$(gcloud config get-value project)
REGION=$(gcloud config get-value ai/region)
BUCKET=$PROJECT_ID # change as necessary
Run the following code as a separate script, it is configured to send about 2,000 trip messages every five minutes with some randomness in the frequency to mimic traffic fluctuations. These numbers come from looking at the historical average of taxi ride frequency in BigQuery.
In production this script would be replaced with actual taxis with IoT devices sending trip data to Cloud Pub/Sub.
publisher = get_pubsub_client(PROJECT_ID, topic="taxi_rides")
while True:
num_trips = random.randint(10, 60)
for i in range(num_trips):
publisher.publish(topic_name, b"taxi_ride")
logging.info("Publishing: %s", time.ctime())
time.sleep(5)
Big Query
Big Query is a Data warehouse managed by google to store, process, analyse, and visualize large amounts of data. Link to read more.
import logging
from google import api_core
from google.cloud import bigquery
def create_dataset(dataset_id="taxifare"):
bq = bigquery.Client()
dataset = bigquery.Dataset(bq.dataset(dataset_id))
try:
bq.create_dataset(dataset) # will fail if dataset already exists
logging.info("Dataset created.")
except api_core.exceptions.Conflict:
logging.info("Dataset already exists.")
def create_table(dataset_id="taxifare", table_name="traffic_realtime"):
bq = bigquery.Client()
dataset = bigquery.Dataset(bq.dataset(dataset_id))
table_ref = dataset.table(table_name)
SCHEMA = [
bigquery.SchemaField("trips_last_5min", "INTEGER", mode="REQUIRED"),
bigquery.SchemaField("time", "TIMESTAMP", mode="REQUIRED"),
]
table = bigquery.Table(table_ref, schema=SCHEMA)
try:
bq.create_table(table)
logging.info("Table created.")
except api_core.exceptions.Conflict:
logging.info("Table already exists.")
Dataflow
Dataflow is a fast, serverless service for executing batch and streaming data processing pipelines. You create your pipelines with Apache Beam and then run them using the Dataflow service. Link to basics of Apache beam & Link to read more about Dataflow.
Now that our taxi data is pushed to Pub/Sub, and our BigQuery table is set up, let’s consume the Pub/Sub data using a streaming DataFlow pipeline.
Dataflow will be responsible for the following transformations:
- Pull the completed trips from the Pub/Sub
- Window the messages (every 5 mins)
- Count the number of messages in the window
- Format the count for BigQuery
- Write results to BigQuery table
import argparse
from datetime import datetime
import apache_beam as beam
from apache_beam.options.pipeline_options import (
GoogleCloudOptions,
PipelineOptions,
SetupOptions,
StandardOptions,
)
from apache_beam.transforms import window # pylint: disable=unused-import
class CountFn(beam.CombineFn):
"""Counter function to accumulate statistics"""
def create_accumulator(self):
return 0
def add_input(self, count, element):
del element
return count + 1
def merge_accumulators(self, accumulators):
return sum(accumulators)
def extract_output(self, count):
return count
def run(argv=None):
"""Build and run the pipeline."""
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument(
"--project", help=("Google Cloud Project ID"), required=True
)
parser.add_argument("--region", help=("Google Cloud region"), required=True)
parser.add_argument(
"--input_topic",
help=("Google Cloud PubSub topic name "),
required=True,
)
known_args, pipeline_args = parser.parse_known_args(argv)
pipeline_options = PipelineOptions(pipeline_args)
pipeline_options.view_as(SetupOptions).save_main_session = True
pipeline_options.view_as(StandardOptions).streaming = True
pipeline_options.view_as(GoogleCloudOptions).region = known_args.region
pipeline_options.view_as(GoogleCloudOptions).project = known_args.project
p = beam.Pipeline(options=pipeline_options)
topic = f"projects/{known_args.project}/topics/{known_args.input_topic}"
# this table needs to exist
table_spec = f"{known_args.project}:taxifare.traffic_realtime"
def to_bq_format(count):
"""BigQuery writer requires rows to be stored as python dictionary"""
return {
"trips_last_5min": count,
"time": datetime.now().strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S"),
}
pipeline = ( # noqa F841 pylint: disable=unused-variable
p
| "read_from_pubsub"
>> beam.io.ReadFromPubSub(topic=topic).with_output_types(bytes)
| "window"
>> beam.WindowInto(window.SlidingWindows(size=300, period=15))
| "count" >> beam.CombineGlobally(CountFn()).without_defaults()
| "format_for_bq" >> beam.Map(to_bq_format)
| "write_to_bq"
>> beam.io.WriteToBigQuery(
table_spec,
# WRITE_TRUNCATE not supported for streaming
write_disposition=beam.io.BigQueryDisposition.WRITE_APPEND,
create_disposition=beam.io.BigQueryDisposition.CREATE_NEVER,
)
)
# result.wait_until_finish() #only do this if running with DirectRunner
result = p.run() # noqa F841 pylint: disable=unused-variable
Launch the dataflow pipeline using the command below.
python3 dataflow.py --input_topic taxi_rides --runner=DataflowRunner --project=$PROJECT_ID --region=$REGION --temp_location=gs://$BUCKET/dataflow_streaming
3. Model Deployment
Vertex AI
Vertex AI is a Jupyter-based fully managed, scalable, enterprise-ready compute infrastructure with security controls and user management capabilities. It serves as a one-stop environment to complete all of the ML work, from experimentation to deployment, to managing and monitoring models. Link to read more
For keeping the article short, I have refrained from explaining the training code. The code can be found in the below GitHub repo. Do let me know in the comments if an explanation of the training code would help.
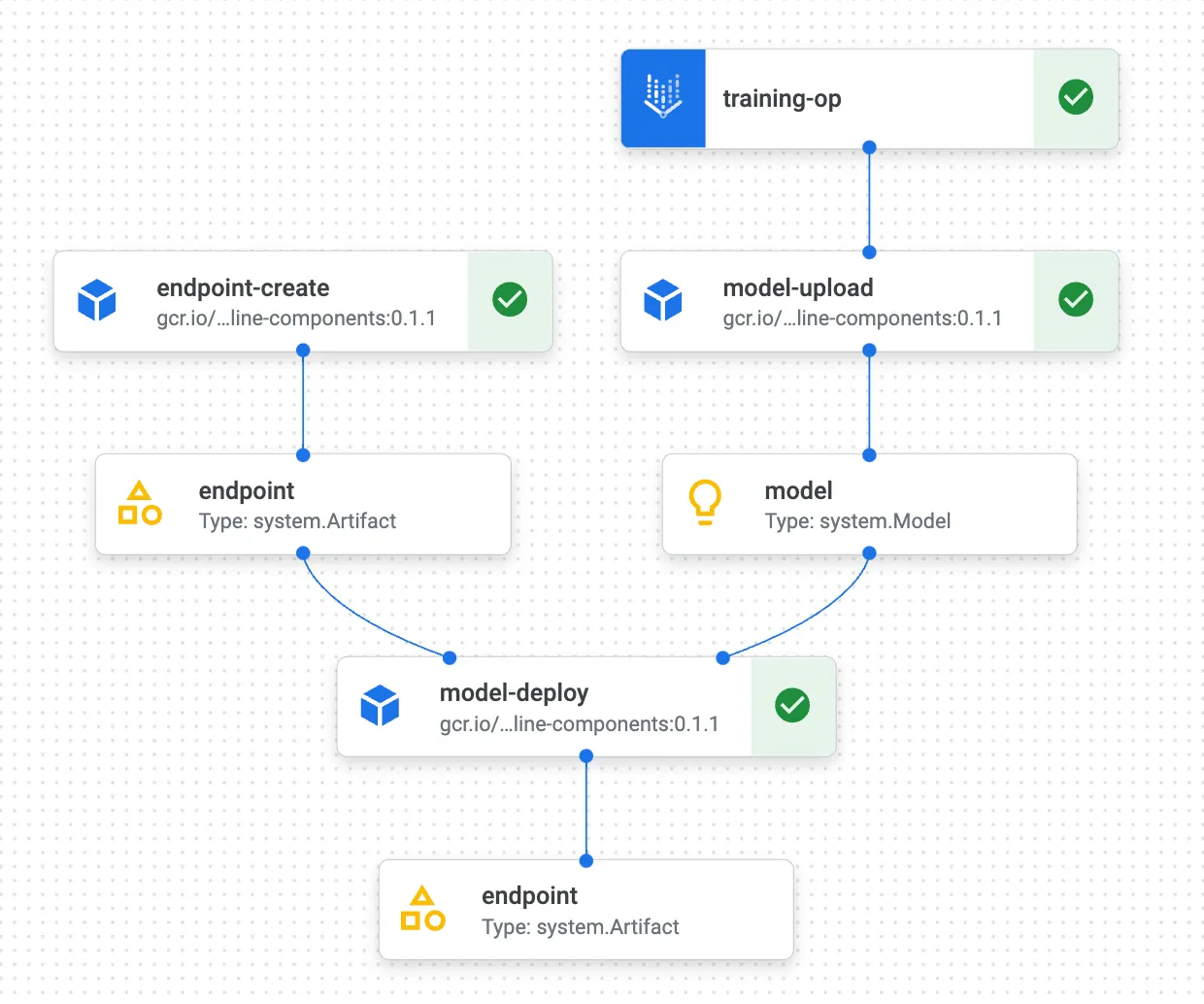
Kubeflow pipeline
Kubeflow is known as the ML toolkit for Kubernetes. The project is dedicated to making deployments of Machine Learning (ML) workflows on Kubernetes simple, portable, and scalable. The goal is to provide a straightforward way to deploy best-of-breed open-source systems for ML in diverse infrastructures.
Link to read more
We will make our prediction service available now. For that, we will be wrapping the following processes as a kubeflow pipeline.
- Model training: Based on the latest labelled data start the model training as a serverless job.
- Upload model: The output of the trained model will be transferred to Google cloud storage.
- Create endpoint: While the model is being trained create an endpoint for the same asynchronously.
- Deployment: Finally deploy the model to the created endpoint.
from kfp.v2.dsl import component, pipeline
from kfp.v2.google import experimental
from google_cloud_pipeline_components.aiplatform import ModelUploadOp, EndpointCreateOp, ModelDeployOp
@component
def training_op(input1: str):
print(f"VertexAI pipeline: {input1}")
@pipeline(name="taxifare--train-upload-endpoint-deploy")
def pipeline(
project: str = PROJECT,
model_display_name: str = MODEL_DISPLAY_NAME,
):
# 1. Model Training
train_task = training_op("taxifare training pipeline")
experimental.run_as_aiplatform_custom_job(
train_task,
display_name=f"pipelines-train-{TIMESTAMP}",
worker_pool_specs=[
{
"pythonPackageSpec": {
"executor_image_uri": PYTHON_PACKAGE_EXECUTOR_IMAGE_URI,
"package_uris": [PYTHON_PACKAGE_URIS],
"python_module": PYTHON_MODULE,
"args": [
f"--eval_data_path={EVAL_DATA_PATH}",
f"--output_dir={OUTDIR}",
f"--train_data_path={TRAIN_DATA_PATH}",
f"--batch_size={BATCH_SIZE}",
f"--num_examples_to_train_on={NUM_EXAMPLES_TO_TRAIN_ON}", # noqa: E501
f"--num_evals={NUM_EVALS}",
f"--nbuckets={NBUCKETS}",
f"--lr={LR}",
f"--nnsize={NNSIZE}",
],
},
"replica_count": f"{REPLICA_COUNT}",
"machineSpec": {
"machineType": f"{MACHINE_TYPE}",
},
}
],
)
# 2. Model Upload
model_upload_op = ModelUploadOp(
project=f"{PROJECT}",
display_name=f"pipelines-ModelUpload-{TIMESTAMP}",
artifact_uri=f"{OUTDIR}/savedmodel",
serving_container_image_uri=f"{SERVING_CONTAINER_IMAGE_URI}",
serving_container_environment_variables={"NOT_USED": "NO_VALUE"},
)
model_upload_op.after(train_task)
# 3. Create Endpoint
endpoint_create_op = EndpointCreateOp(
project=f"{PROJECT}",
display_name=f"pipelines-EndpointCreate-{TIMESTAMP}",
)
# 4. Deployment
model_deploy_op = ModelDeployOp(
project=f"{PROJECT}",
endpoint=endpoint_create_op.outputs["endpoint"],
model=model_upload_op.outputs["model"],
deployed_model_display_name=f"{MODEL_DISPLAY_NAME}",
machine_type=f"{MACHINE_TYPE}",
)
# Compile the pipeline
from kfp.v2 import compiler
if not os.path.isdir("vertex_pipelines"):
os.mkdir("vertex_pipelines")
compiler.Compiler().compile(
pipeline_func=pipeline,
package_path="./vertex_pipelines/train_upload_endpoint_deploy.json",
If the compilation is successful then you can run the following code and your pipeline will start running.
# Run the pipeline
from google_cloud_pipeline_components import aiplatform
pipeline_job = aiplatform.pipeline_jobs.PipelineJob(
display_name="taxifare_pipeline",
template_path="./vertex_pipelines/train_upload_endpoint_deploy.json",
pipeline_root=f"{PIPELINE_ROOT}",
project=PROJECT,
location=REGION,
)
pipeline_job.run()
Once the pipeline starts, head to Vertex AI > Pipeline and you should be able to see the pipeline similar to the below screenshot.

4. Prediction
From the previous step, save the endpoint(ENDPOINT) where our model is deployed. We need only two more components to make this system complete.
- A function that would fetch the last 5 min traffic and add it as a feature to the request.
- Another function is to pass on the modified request, create the prediction service client and present the result.
import logging
from typing import Dict, List, Union
from google.cloud import aiplatform, bigquery
from google.protobuf import json_format
from google.protobuf.struct_pb2 import Value
def add_traffic_last_5min(instance, dataset="taxifare", table="traffic_realtime"):
""" Adds the dynamic feature `traffic_last_5min` to the instance
"""
bq = bigquery.Client()
query_string = f"""
SELECT
*
FROM
`{dataset}.{table}`
ORDER BY
time DESC
LIMIT 1
"""
trips = bq.query(query_string).to_dataframe()["trips_last_5min"][0]
instance["traffic_last_5min"] = int(trips)
return instance
def predict(
project: str,
endpoint_id: str,
instances: Union[Dict, List[Dict]],
location: str = "us-central1",
api_endpoint: str = "us-central1-aiplatform.googleapis.com",
):
"""
`instances` can be either single instance of type dict or a list
of instances.
Reference: https://github.com/googleapis/python-aiplatform/blob/master/samples/snippets/predict_custom_trained_model_sample.py
"""
client_options = {"api_endpoint": api_endpoint} # f"{REGION}-aiplatform.googleapis.com"
client = aiplatform.gapic.PredictionServiceClient(client_options=client_options)
instances = instances if type(instances) == list else [instances]
instances = [add_traffic_last_5min(instance_dict) for instance_dict in instances]
instances = [
json_format.ParseDict(instance_dict, Value()) for instance_dict in instances
]
parameters_dict = {}
parameters = json_format.ParseDict(parameters_dict, Value())
endpoint = client.endpoint_path(
project=project, location=location, endpoint=endpoint_id
)
response = client.predict(
endpoint=endpoint, instances=instances, parameters=parameters
)
logging.info("response")
logging.info(f" deployed_model_id: {response.deployed_model_id}")
# The predictions are a google.protobuf.Value representation of the model's predictions.
predictions = response.predictions
for prediction in predictions:
logging.info(" prediction:", dict(prediction))
Now you are ready to hit the endpoint and receive the prediction.
instance = {
"dayofweek": 4,
"hourofday": 13,
"pickup_longitude":-73.99,
"pickup_latitude": 40.758,
"dropoff_latitude": 41.742,
"dropoff_longitude": -73.07
}
predict(PROJECT_ID, ENDPOINT, instance)
You can refer to my repository for the complete code: 💻 Code.