Booking.com's RS
Summary of Booking.com's RS, their Machine Learning Productionization System.
🛐 One of the Core ideas of booking.com: "Diversity gives us strength".
🥕 Requirements:
- Consistency: online predictions and offline should match
- High availability: system available 24/7
- Low latency: real-time or near real-time predictions
- Scalability: Should be able to handle multiple requests simultaneously.
- Observability: Monitor input and output space.
- Reusability: The same model can be used in multiple places eg: a family-friendly hotel predictor can be used on the home page and in many filters.
👨👨👦👦 The fantastic four approach
-
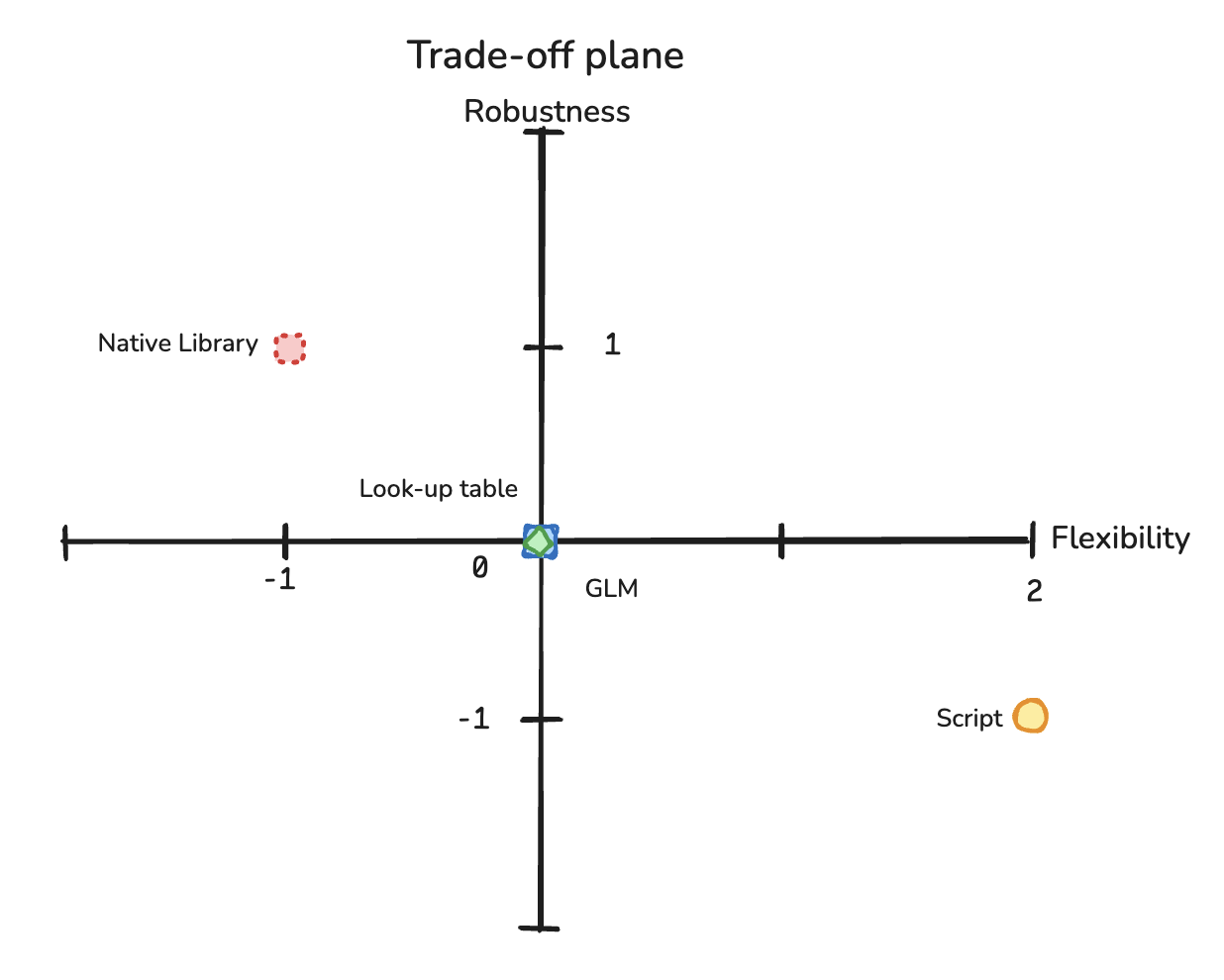
Lookup tables: ▴ Precompute all the possible input vectors and save them as key-value pairs. For a prediction, they have to just look up. It is Low latency, horizontally scaleable - Implemented using the Cassandra key-value store (or in memory if they are small enough). Disadvantages: ▴ Computation overhead and possibly resource wastage, even more, difficult with newer model versions. Usage: ▴ Discrete input space cases, User / accommodation / destination identifiers.
-
Generalized Linear Models (GLMs): ▴ The model representation is stored in the linear form of weight and bias and computed when needed. Can also be SVMs. So continuous input. - It doesn’t matter which training algorithm is used as long as it can be represented by a weight vector, an input transformation and link function, it can be run in production. ▴ Inner product < vectorize(X), W> ▴ Argsort for ranking the results based on the score Disadvantage: ▴ An extra step, once trained convert to linear form. Usage: ▴ User context models, destination, recommendations, etc
-
Native libraries: ▴ Most straightforward approach: Train the model to serialize it and deserialize before serving. Disadvantage ▴ It has latency issues, this is usually optimized for training and not necessarily for serving. Usage: ▴ Tree-based model, GBT, NN
-
Scripted models: ▴ A script is invoked during the request which gives the flexibility to control output for cases like post-processing. ▴ Flexibility for post-processing. Disadvantage ▴ Each line of code will determine the online request lifecycle latency. Usage ▴ For unsupported libraries and models with extra logic.
Reference: Booking.com's RS